【C++基础】06 运算符
【C++基础】06 运算符
recode之前我们讲到了基本的运算符,这些运算符对上面计算的运算符进行补充
1. 逻辑运算符
1.1. 与(&&)运算
遵循逻辑“有假必假”
例如:
(1 && 1) ==> true =1 |
1.2.或(||)运算
遵循逻辑“有真必真“
1.3. 非(!)运算
!0 ==> 1 |
与的优先级高于或
同时出现先计算与
优先级:或 < 与 < 非
2. 逗号运算符
逗号运算符的级别是最低的,输出以逗号分割最后的一个数;
看如下一段代码:
|
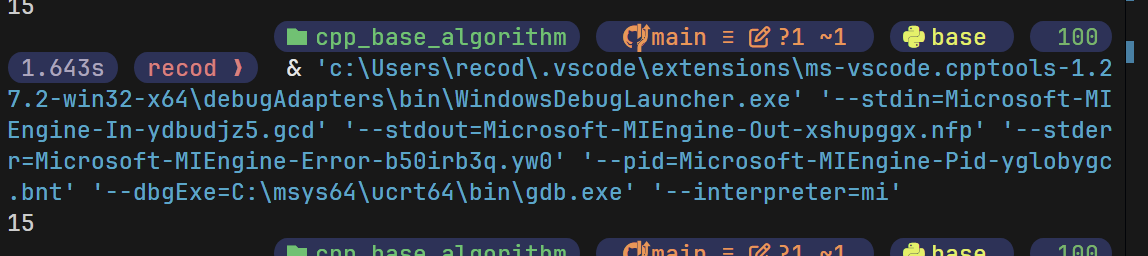
我们预想中输出的结果为:2
但我们运行一下
输出为15
这是为什么呢???
这是因为我们程序对字符分割的理解出现了问题
程序默认的分割是:
|
所以输出为(a = 7+8)
如果我们想输出2
则我们应对程序的结构重新进行分割
|
案例:
对变量进行交换
首就是尾,尾就是首
需要注意赋值和分隔的顺序,因为
,的优先级比赋值运算符还低
3.位运算符
评论
匿名评论隐私政策
✅ 你无需删除空行,直接评论以获取最佳展示效果